5 REASONS YOUR FICO SCORE IS LOW
I will show you the 5 reasons your FICO score is low.
They are directly related to criteria FICO uses to calculate your score.
Most of America has a credit score below 600.
Over 70% of credit reports contain errors.
What does that mean for you and your credit score?
It could mean negative items are erroneously damaging your credit score.
Again, Why is your score low? How do you improve your score? Let’s talk about it!
WHAT IS FICO?
To understand the big picture it’s imperative to know who and what FICO is.
FICO stands for, and used to be called Fair Isaac and Company.
It’s a data analytics company that created a credit scoring model that is the most widely recognized and used by creditors.
It’s a publicly traded business that was founded in 1956 by William Fair and Earl Isaac, and the headquarters are currently based in San Jose, CA.
The very first general purpose FICO score was released to public in 1989.
FICO scores are based on credit reports primarily from the big three, Equifax, TransUnion, and Experian.
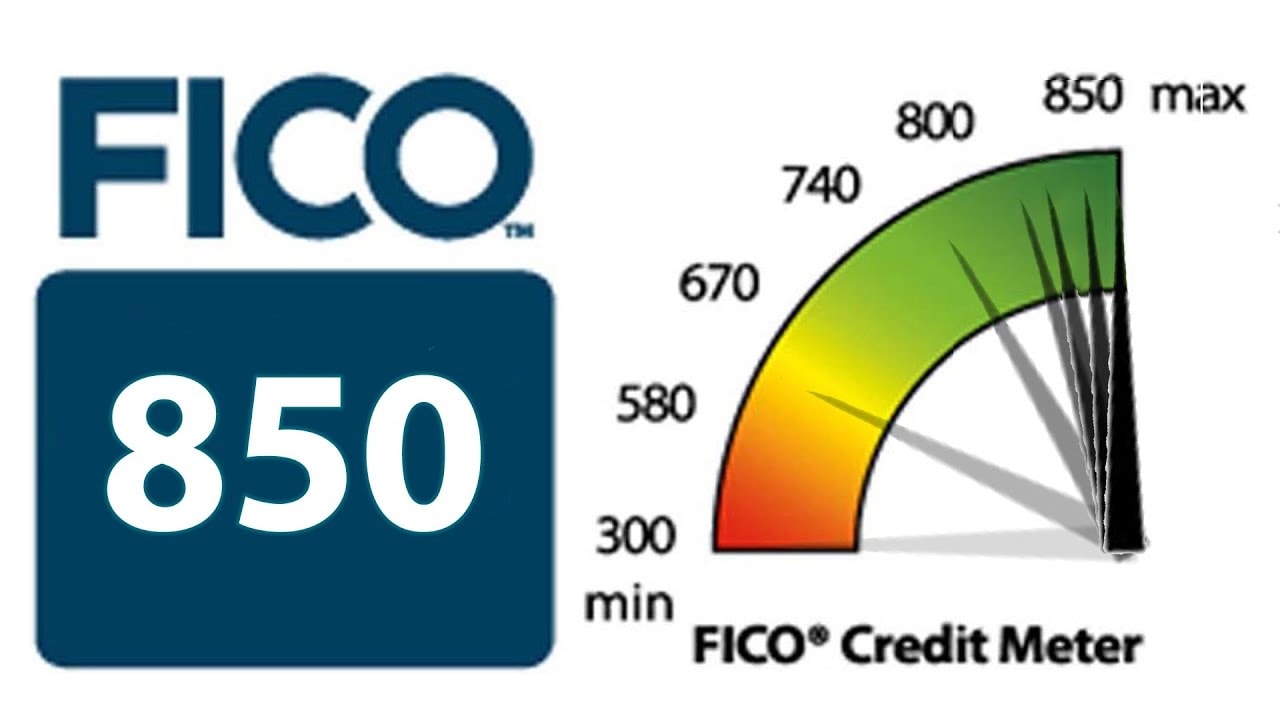
Base FICO scores have a range of 300 to 850. These scores are used by lenders to determine the creditworthiness of potential borrowers.
In other words, the FICO score tells lenders the probability a borrower will default on payment.
WHAT IS A CREDIT BUREAU?
Credit bureaus are also known as credit reporting agencies, and like FICO they too are in the data gathering business.
Also, like FICO they are individual companies and not government controlled.
The most commonly known and used credit bureaus are Equifax, TransUnion, and Experian.
A credit bureau is a data collection agency that collects account information from tons of creditors and distributes that information to other creditors to assist them with assessing a borrower’s credit worthiness.
The information provided by the credit bureaus also assists FICO in calculating credit scores.
Creditors spend a lot of money paying for consumers debt payment history.
They also spend tons of money reporting the information to the bureaus as well.
Credit bureaus are paid to give credit reporting data, and also to receive it from lenders.
Great deal that they worked out for themselves,but where does that leave you at?
HOW DOES FICO CALCULATE YOU SCORE?
This is where things get a little tricky. Nobody really knows exactly how FICO calculates credit scores.
However, FICO did provide the criteria for their calculation. It’s broken down into 5 factors.
Payment history, credit utilization, length of credit, new credit, and credit mix.
Those 5 factors are the 5 reasons your credit score is low, or high depending how you fair.
The breakdown is as follows:
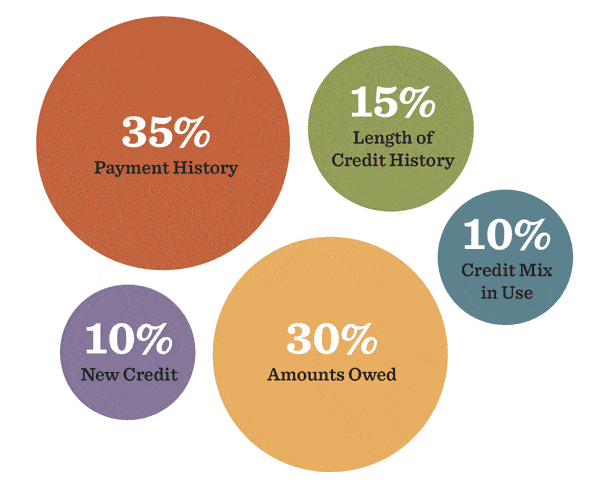
- 35% Payment History
- 30% Credit Utilization/Amounts Owed
- 15% Length of Credit History
- 10% New Credit
- 10% Credit Mix
PAYMENT HISTORY
Payment history is responsible for 35% of your FICO score, which is nearly worth 200 points.
Let’s break down that calculation. Remember, FICO has the credit score range from 300 to 850.
A credit score begins at 300 and maximizes at 850, leaving 550 points in between.
Calculation:
550 x .35 = 192.5 Points from Payment History
As you can see, payment history is very important, and the largest credit score factor.
Here are some negative credit items that can damage your FICO score tremendously:
- 30, 60, 90, and 120 days late payments
- Charge-Off
- Collections
- Repo
- Foreclosure
Late payments are very damaging to your FICO score. They can lower your score by more than 100 points.
Keep in mind that a late payment is only reported to credit bureaus when it is 30 days past due or more.
Lenders report 30, 60, 90, and 120 days late payments.
A payment made 5 days late, 15 days, or even 29 days late will not be reported by lenders.
Lenders Charge-Off a debt after non payment of 180 days or more.
The charge-off is a write off for tax purposes, then usually they hire a collection agency to collect payment, or they sell them the debt.
Collection agencies are either hired by your lender or they buy your debt for pennies on the dollar and attempt to collect.
Collections are reported generally when you have not paid your original creditor for 180 days or more.
Repos are also a result of non-payment of 180 days or more.
A foreclosure occurs when you have a mortgage loan you have not paid for 180 days or more.
Every one of them are negative items that lenders report to credit bureaus and will greatly damage your FICO scores.
CREDIT UTILIZATION
The second largest factor of your FICO score is credit utilization, also called amounts owed.
This is the ratio of debt balance divided by available credit on your credit cards.
Also known as debt to credit ratio.
FICO breaks it down in two parts. First part consists of individual credit card utilization, second part consists of total credit card utilization.
The ideal credit utilization rate is 30% or below.
According to FICO, the optimal rate is between 1-3%.
So, for example, if you have a credit card with a $1,000 limit, you would like the balance to never be reported at over $300.
Ideal balance would be $300 or less, which is 30% or less on a credit card with a credit limit of $1,000.
Below is the equation of the point total credit utilization is responsible for.
Calculation:
550 x .3 = 165 Points from Credit Utilization
That is a significant amount of points, and many consumer/borrowers are missing out on a higher credit score because their credit cards are maxed out.
Many clients of mine only need to pay down their credit card balances to get in the 700 and above club.
Something that needs to be understood that many get wrong is that loans do not factor into credit utilization.
That is a misconception that I hear often. In fact, credit utilization only pertains to credit card debt.
Not mortgage loan, auto loan, or any loan debt. Loans, also known as installments, factor into payment history.
Credit cards, also known as revolving accounts, impact both payment history and credit utilization.

LENGTH OF CREDIT HISTORY
The third most impactful FICO score factor is your length of credit history.
It’s worth 15% of your credit scores. To maximize your score you must have what in the industry is called seasoned tradelines.
To be considered seasoned, the tradeline must be at least 24 months old.
A tradeline is any line of credit a lender extends to a borrower.
This can be a credit card, auto loan, mortgage/home loan, or even a home equity line of credit or retail credit card.
They all qualify. Basically any form of credit is a tradeline.
Below you will see how many points you can potentially earn from this factor.
Calculation:
550 x .15 = 82.5 Points from Length of Credit History
The length of credit history averages out the median of your existing credit cards.
For example, a person with two credit cards, one being 10 years old, and the second being brand new would have a 5 year length of credit history.
Equation: 10yr credit card + 0yr credit card / 2 credit cards = 5 years (length of credit history)
Typically, you would want to be around 5 years and up, 2 years and up is the minimum to really score significant points.
CREDIT MIX
Credit mix is only worth 10% of your FICO score, but must be maximized if you want to ever reach the upper echelon of credit scores.
FICO rewards you for having both types of credit, revolving accounts and installment accounts.
Meaning credit cards and any type of loan. Putting together the right credit mix can earn you points.
Below you can see just how many points you can potentially earn from this FICO factor.
Calculation:
550 x .1 = 55 Points from Credit Mix
To really squeeze the points out of credit mix you need to really have more than one of each.
Ideally, you would want to have 4 credit cards and at least 2 loans.
That would give you 6 tradelines that have a really good credit mix.
Please refer to the “THE 4 CREDIT CARD METHOD” blog post to learn my strategy for improving and also maximizing your your credit score total to upwards of 800 points.
NEW CREDIT
The final FICO factor that affects your score is new credit.
New credit is another 10% of your FICO score, which is really referring to inquiries.
Below you can see how many points you can gain from this FICO factor.
Calculation:
550 x .1 = 55 Points from New Credit
When you apply for a credit product, whether it be a loan or credit card, the lender performs a hard credit pull.
This transaction is performed, recorded and reported by a credit bureau of the lenders choosing.
Each time an inquiry is performed you lose points. There are different opinions on how many points an inquiry actually costs you. I tend to go with 2-5 points per inquiry.
That can add up quickly if you are applying for several credit products in a short amount of time.
It’s best to apply for credit when you have a really good credit score for two reasons.
One, you will get the best interest rates, and two, you are less likely to be denied.
Just think of it as the price you pay for an opportunity to obtain a new credit card or loan.
When your credit application is being denied and you apply for more and more credit products you will lose a lot of points.
CONCLUSION
After learning the 5 reasons you FICO score is low you should be much better prepared to avoid the traps.
Make sure you are working towards strengthening your credit profile by addressing any weaknesses that relate to FICO’s criteria:
- Payment History
- Credit Utilization/Debt to Credit Ratio
- Length of Credit History
- Credit Mix
- New Credit
Here are some tips on how you can increase your FICO scores:
- Make payments on time, do not allow any account to go 30 days late
- Keep credit card balances below 30% of the credit limit, but do not zero out balance
- Never close accounts, keep them open to increase credit history
- Obtain at least 4 credit cards and two loans to keep a good credit mix
- Do not continue to apply for credit products if you have been denied more than once
If you follow the above advice you will end up earning yourself a spot in the 700 club and possibly a spot in the 800 club.
CREDIT TALK RELATED BLOGS
5 REASONS YOUR FICO SCORE IS LOW